Phase 1 - Expert Consultation
- Definition of the project’s aim
- Thorough discussion of the antigen characteristics
- Support in antigen design
- Definition of screening set-up (inhibition tests and/or screenings of cross-reactants)
Anti-idiotypic antibodies (anti-IDs) are used in preclinical and clinical research of therapeutic antibodies and biosimilars as well as in antibody drug development studies. Anti-IDs allow the reliable monitoring and quantitation of antibody drugs in clinical samples and the detection of antibody drugs that closely resemble circulating human immunoglobulins.
Ever since the first findings on antibodies being able to specifically recognize the idiotype of a target antibody were published in the 1950s, anti-idiotypic antibodies have become more and more important for preclinical and clinical research and made their way into specific forms of therapy.
The idiotype is the collective set of idiotopes which are the antigenic determinants, formed by the VL and VH chain of the hypervariable region within the Fab fragment of an immunoglobulin. Idiotopes can occur either in close proximity to the paratope or be partially overlapping. In general, idiotopes are clonally unique to antibodies, and therefore anti-IDs are specific to only one antibody.
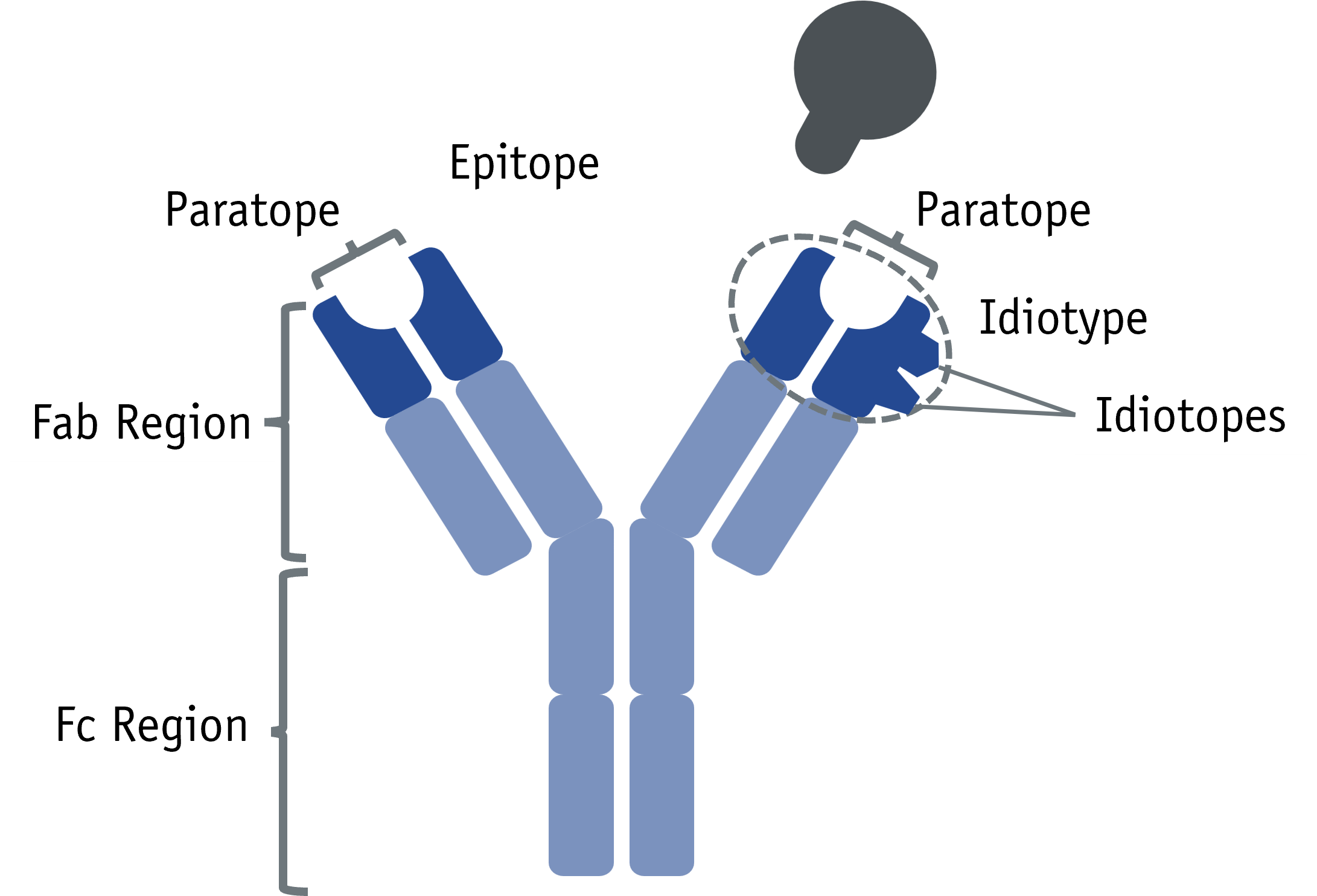
Anti-IDs can be divided into three subgroups, according to their primary binding target. Non-inhibitory anti-IDs bind the target antibody by any idiotype on the VL or VH chain situated outside the paratope, preserving the original antigen- binding properties. Inhibitory anti-IDs bind the target antibody via the paratope and thus inhibit the binding to its antigen. Complex-binding anti-IDs show affinity to the target antibody upon its prior binding to the antigen as a prerequisite, thus also having a non-inhibitory nature.
Monoclonal anti-IDs are routinely used as capture and detection reagents in pharmacokinetic (PK) assays for the quantification of antibody drugs in patients’ serum. They are highly specific and have the advantage that time-consuming IgG depletion is not necessary. In addition, monoclonal anti-IDs provide reproducible results (lot-to-lot consistency) and can be produced indefinitely.
BioGenes offers the development of anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibodies (specific anti-drug-antibodies) according to an optimized hybridoma technology in mice. Our specialists have successfully developed monoclonal anti-IDs against human, humanized and chimeric therapeutic antibodies that are used for the quantification of antibody drugs in patient serum.
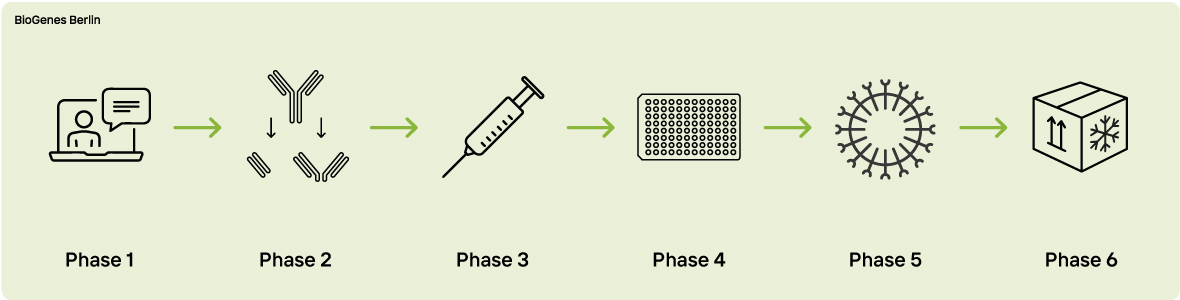
Phase 1 - Expert Consultation
Phase 2 - Antigen Preparation
Phase 3 - Immunization
Phase 4 - Cell fusion & hybridoma screening
Phase 5 - Cloning
Options:
Phase 6 - Delivery & preservation
After finalization of the project the materials generated (clones, cryo cultures, antibodies, remaining antigens) within the project are solely owned by the customer.
Polyclonal anti-IDs can be used as detection reagents in PK assays but are most commonly used as positive controls in immunogenicity assays.
The immunogenicity assays are performed to assess unwanted immune reactions in patients after treatment with a therapeutic antibody. This involves the use of anti-IDs as a positive assay control and should therefore represent the whole spectrum of ADAs to a biotherapeutic product. Individual monoclonal anti-IDs might not adequately represent the entire range of ADAs as occurring during an unwanted immune response. In contrast to monoclonal anti-IDs, polyclonal anti-ID antibodies represent an entire spectrum of epitopes when purified against the therapeutic antibody and additionally depleted of cross-reactive anti-human-IgG antibodies.
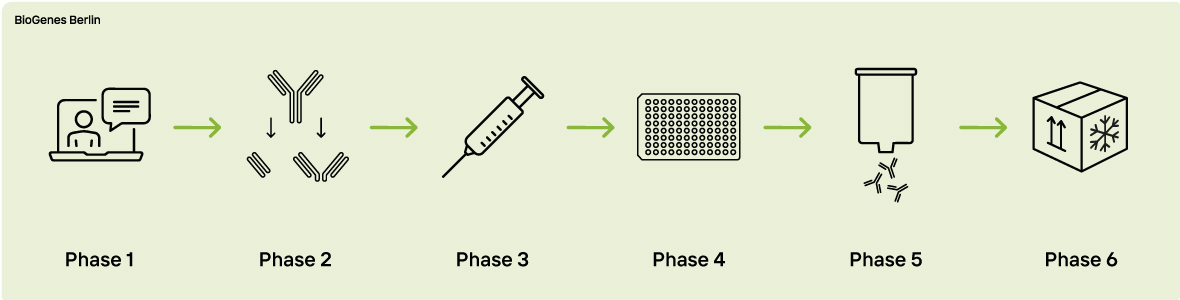
Phase 1 - Expert Consultation
Phase 2 - Antigen Preparation
Phase 3 - Immunization
Phase 4 - Titer Determination
Phase 5 - Affinity Purifications
Phase 6 - QC and Delivery
Contact
If you need more information, a specific offer
or want to talk to an expert
Newsletter
Keep me updated